Ordinary Leeds Line
Ordinary Leeds Line
Definition
Litz wire consists of multiple strands of insulated wire and is widely used in applications requiring good flexibility and high-frequency performance. High-frequency litz wire is made by twisting multiple insulated strands together, typically used in applications with operating frequencies between 10kHz and 5MHz. In the application of magnetic energy storage coils, high frequency can cause eddy current losses. Eddy current losses increase with the frequency of the current, and these losses are caused by the skin effect and proximity effect. High-frequency litz wire can effectively reduce the losses caused by the 'skin effect' and 'proximity effect' in high-frequency applications.
Single insulated wire
The basic unit of litz wire is a single enameled wire, which can be optimized in various combinations of conductor materials and insulating materials to meet different application needs.
Structure
The number of strands in a single enameled wire can be twisted once or multiple times, allowing for various design choices in the structure of litz wire.
Additionally, various forms of outer insulating materials can be combined based on application needs, such as coating films (PET, PEN, PPS, PI, etc.), coated fibers (natural silk, nylon, polyester, etc.), and extruded materials.
Types of litz wire
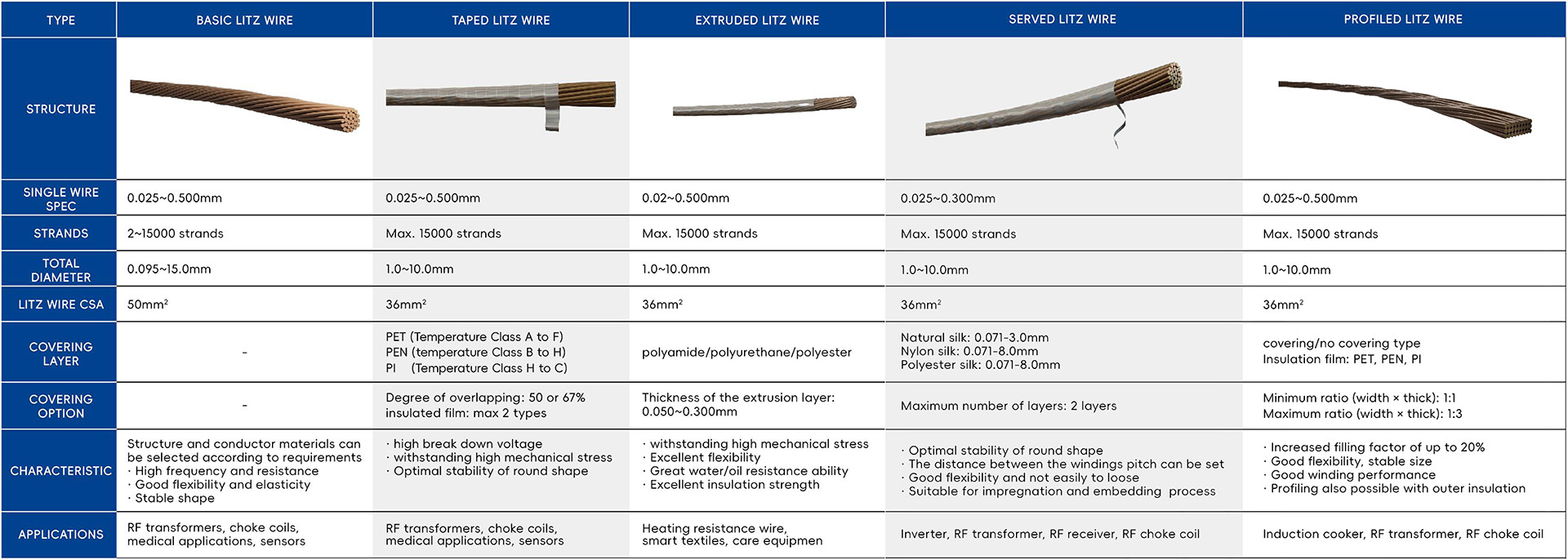
Product Features
Application Area
Based on the number of strands of a single enameled wire, it can be twisted once or multiple times, allowing for various design options in the structure of Leeds wire. Additionally, various forms of outer coating materials can be combined on the outer layer according to application needs, such as coating films (PET, PEN, PPS, PI, etc.), coating fibers (natural silk, nylon, polyester, etc.), and extruded material coatings.
Production Scope
Table Download
Advantages Of Huaye
Dongguan Base
Tel: +86-769-8223-6800
Contact: Mr. Deng +86-158-1685-6940
Contact person: ms fan +86-135-0980-6566
Address: No.4, No.6 Road, Jinshagang, Dalang Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province
Xianning Base
Tel: +86-715-8101-600
Contact: Mr. Peng +86-150-6858-9744
Contact:Ms. Xu :+86-136-3163-8124
Address: Building 2, No. 769 He Sheng Road, High-tech Yangtze River Industrial Park, Xianning City, Hubei Province (Intelligent Manufacturing Industrial Park)
Copyright © Hubei Zhongke Huaye New Material Technology Co., Ltd.
This website supports IPV4 / IPV6 bidirectional access


